Physiotherapy, as an integral part of medical rehabilitation, plays a key role in managing inflammation in patients. Inflammation is often associated with a number of diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis and even cardiovascular disease. Physical therapy can help relieve symptoms and speed up the healing process.
Mechanisms of action
Physiotherapy uses various methods and techniques that help reduce inflammation, such as manual therapy, therapeutic exercises, heat and cold therapy, ultrasound and electrotherapy. These techniques are intended to reduce pain, improve mobility, increase muscle strength, and improve the overall performance of the body.
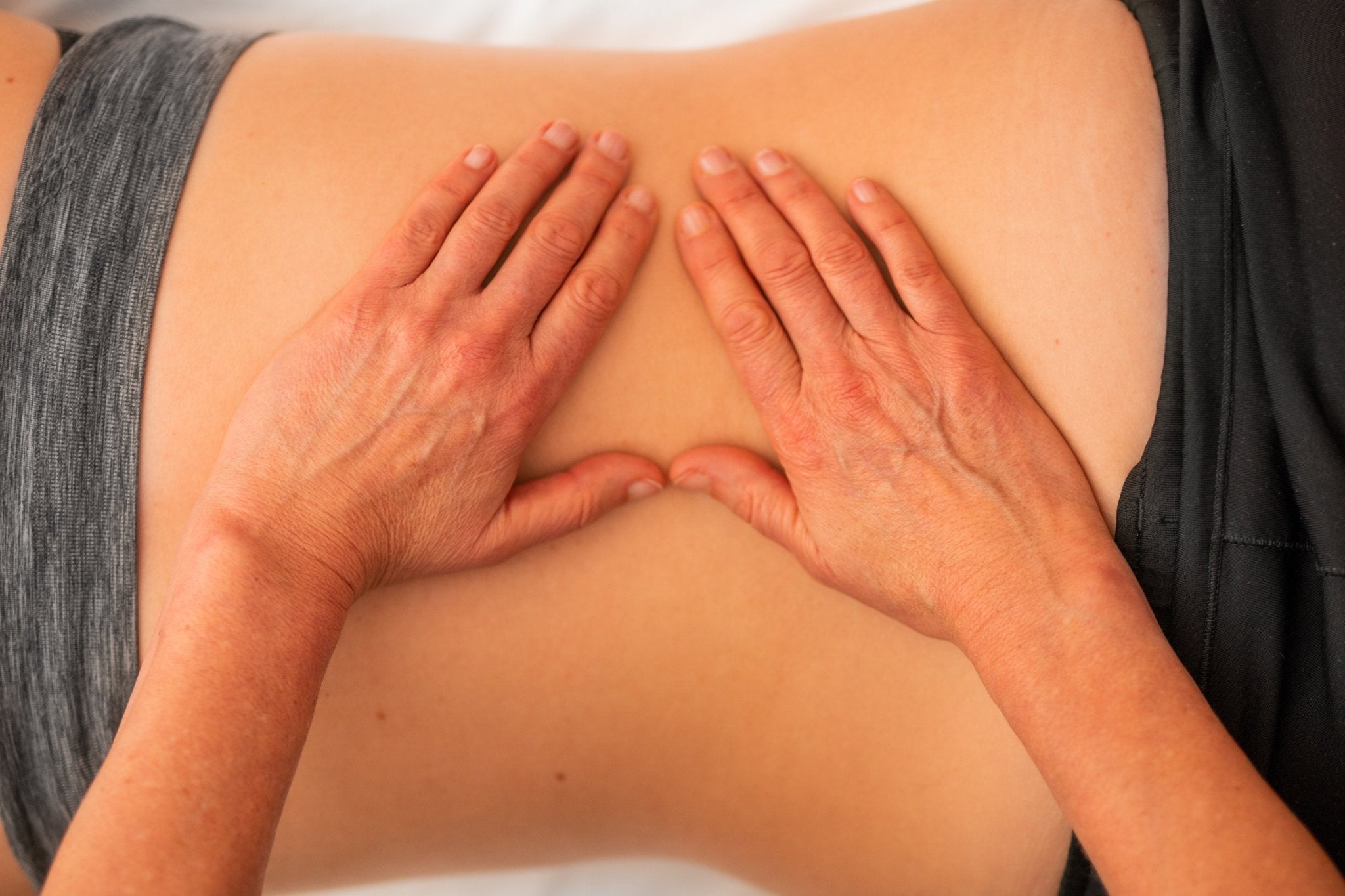
Manual therapy
Manual therapy, which includes massage and joint mobilization, helps reduce inflammation by improving circulation and reducing muscle tension. Improving circulation helps deliver nutrients to the inflamed area and speeds up the removal of waste products, which speeds up the healing process.
Therapeutic exercises
Therapeutic exercises are a key element of physiotherapy. They help maintain and improve range of motion, increase muscle strength and improve the overall performance of the body. Regular exercise can also help reduce inflammation by increasing the production of the body's natural pain-relieving and anti-inflammatory substances, such as endorphins.
Heat and cold therapy
Heat and cold therapy are often used to reduce inflammation. Heat helps increase blood circulation, which speeds up the healing process, while cold helps reduce pain and swelling.
Electrotherapy and ultrasound
Electrotherapy and ultrasound are other popular techniques used in physical therapy. Electrotherapy uses electrical current to stimulate nerves and muscles, which helps reduce pain and swelling. Ultrasound, by producing a sound wave, can help reduce inflammation by improving blood circulation and stimulating healing processes.
Physiotherapy is therefore a key element in the treatment and management of inflammation. By using appropriate techniques, physiotherapy helps reduce pain and swelling, increases range of motion and improves patients' quality of life. However, it is important to remember that physical therapy is part of a comprehensive treatment plan and should be used in conjunction with other forms of therapy such as anti-inflammatories and lifestyle changes.
Patryk Pyrz